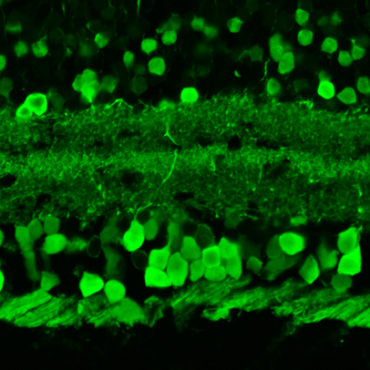
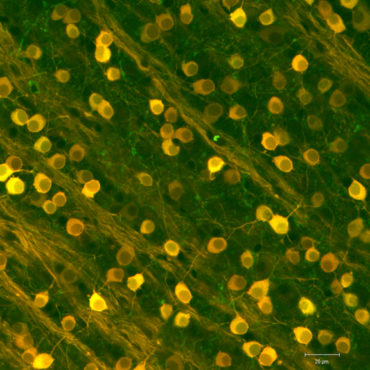
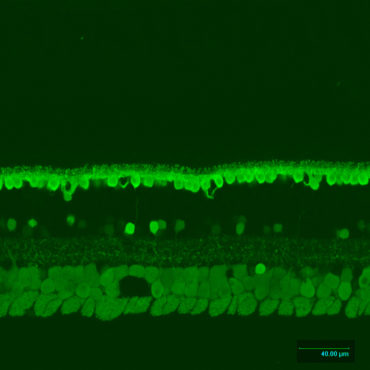
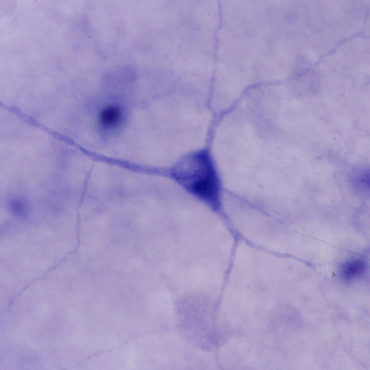
Ganglion cells
Ganglion cells are a type of neuron located near the inner surface of the retina and are the final output neurons of the vertebrate retina. Ganglion cells collect visual information in their dendrites from bipolar cells and amacrine cells and transmit it to the brain through out their axon to the brain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation. Based on their projections and functions, there are at least five main classes of retinal ganglion cells: Parasol (Magnocellular, or M pathway). Midget (Parvocellular, or P pathway). Bistratified (Koniocellular, or K pathway). Photosensitive ganglion cells (melanopsin ganglion cells). Ganglion cells projecting to the Superior Colliculus for eye movements (saccades).